Recurrent Neural Network
Giới thiệu (Introduction)
Recurrent Neural Network là một loại mạng nơ-ron được thiết kế để xử lý dữ liệu dạng chuỗi, như chuỗi thời gian, ngôn ngữ, hoặc khung hình video. Khác với mạng nơ-ron truyền thống, RNN có các kết nối vòng lặp (loop back) cho phép nó “ghi nhớ” các đầu vào trước đó. Điều này giúp RNN rất phù hợp cho các bài toán như mô hình ngôn ngữ, nhận diện giọng nói, và dự đoán chuỗi.
Các biến thể như LSTM và GRU đã được phát triển để giải quyết các thách thức khi huấn luyện RNN, đặc biệt là việc ghi nhớ các phụ thuộc dài hạn (long-term dependencies) trong dữ liệu. Chúng ta sẽ bàn về các biến thể này ở bài sau.
Mô hình ngôn ngữ
Mô hình ngôn ngữ là một hệ thống trí tuệ nhân tạo được thiết kế để hiểu, sinh hoặc dự đoán ngôn ngữ con người dựa trên các mẫu và cấu trúc học được từ lượng lớn dữ liệu văn bản. Nó giống như một “nhà ngôn ngữ học ảo” xử lý và sinh văn bản, hỗ trợ các tác vụ như dịch, tóm tắt, hội thoại… 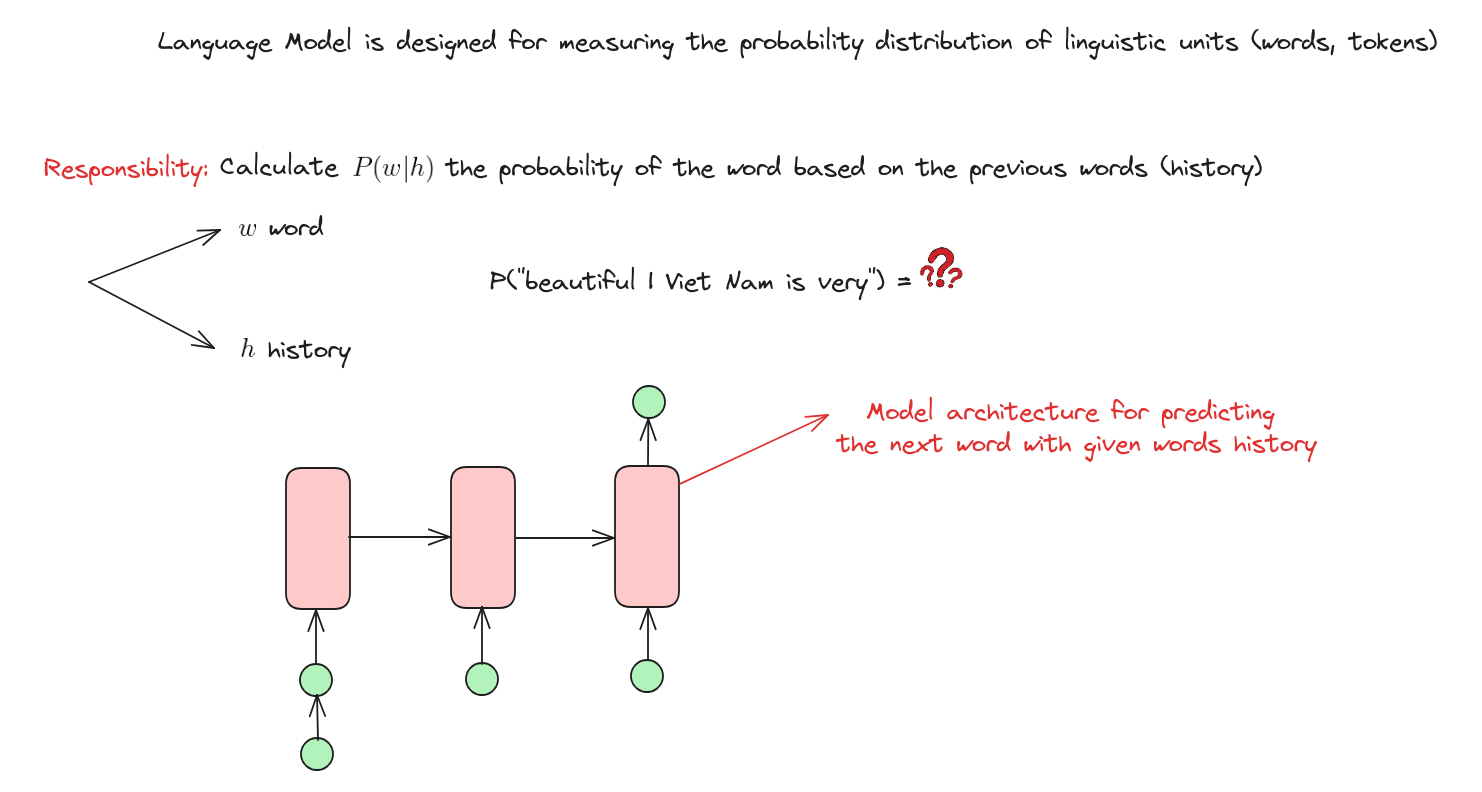
Mô hình ngôn ngữ N-Grams
N-Grams
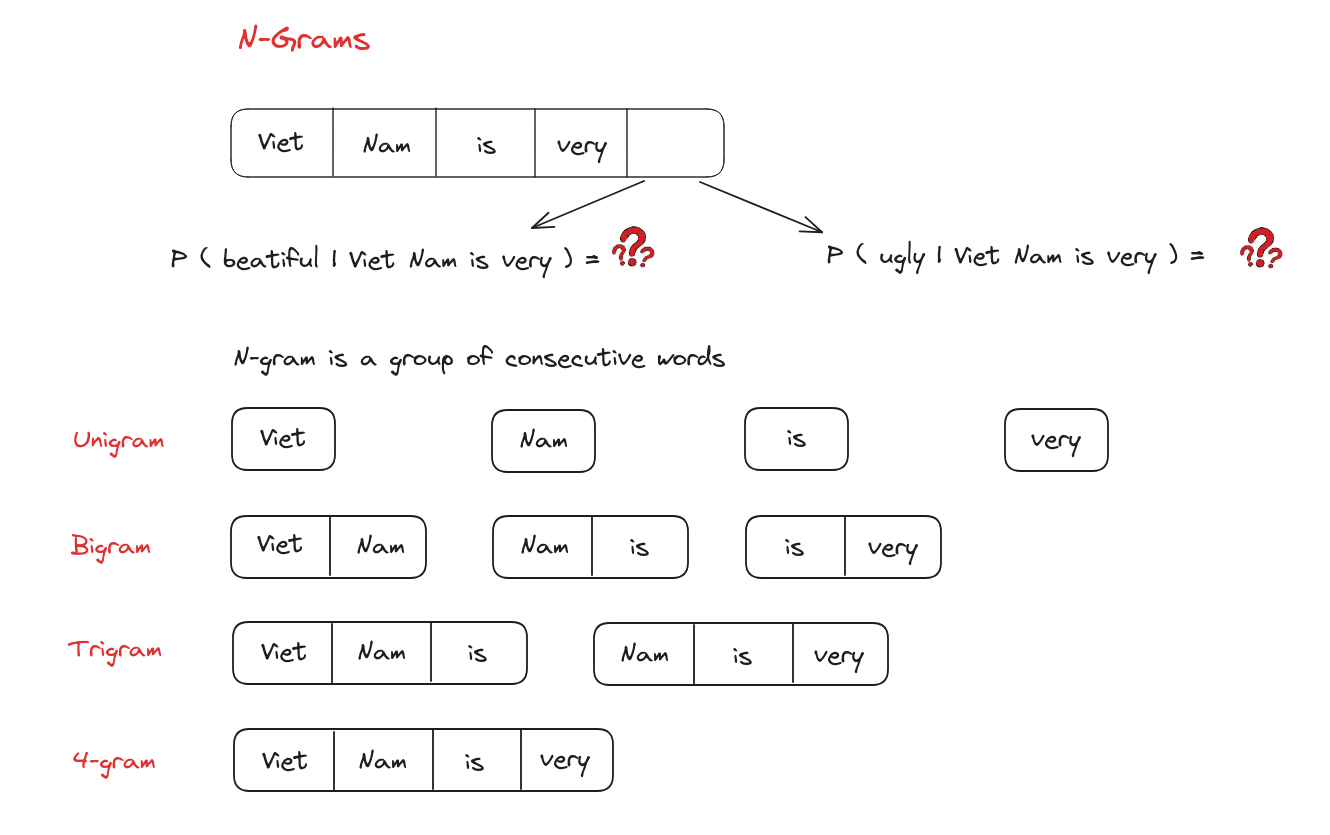
Mô hình N-Grams
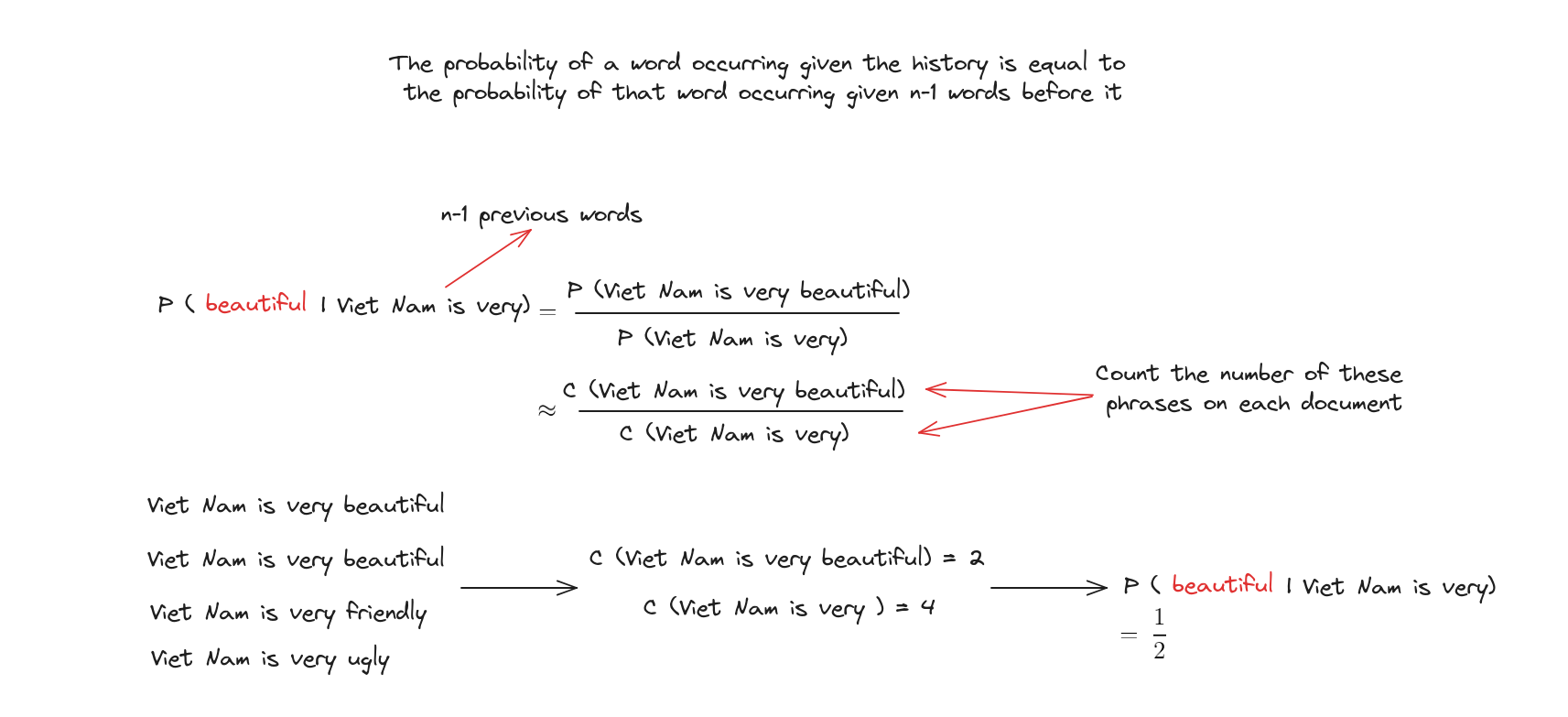
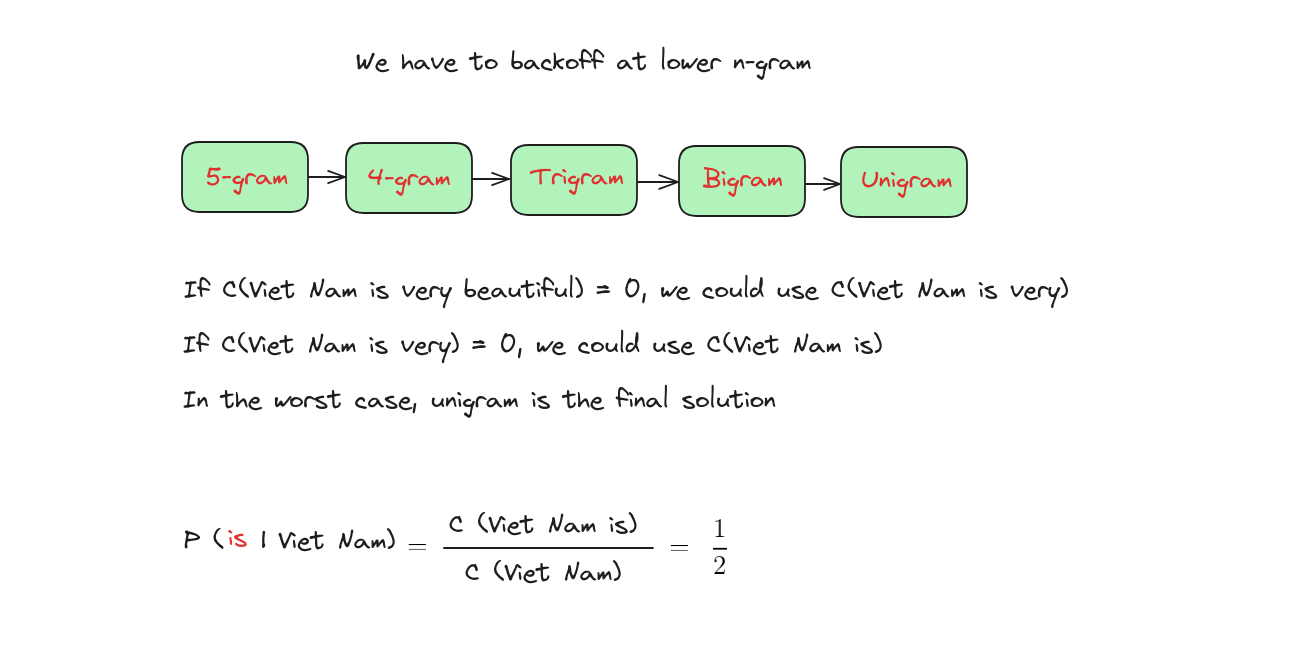
Vấn đề của N-Grams
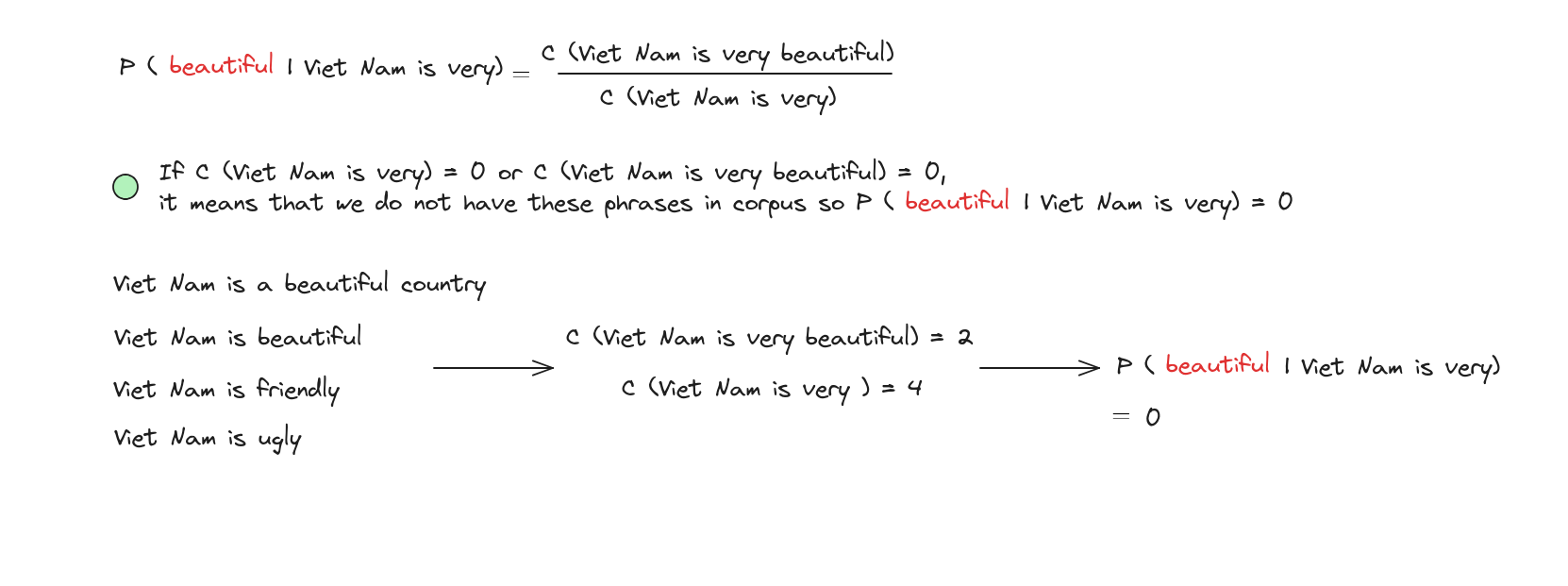
Giải pháp cho N-Grams
Điểm yếu của N-Grams
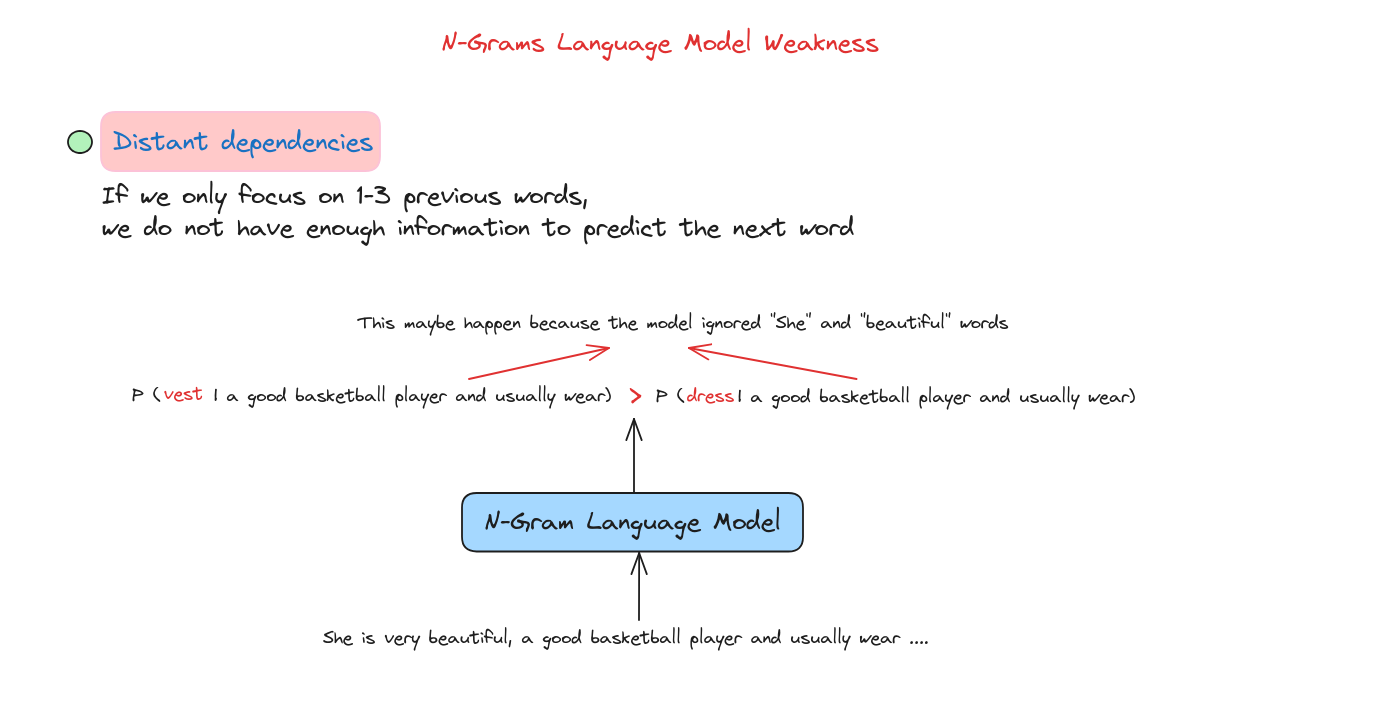
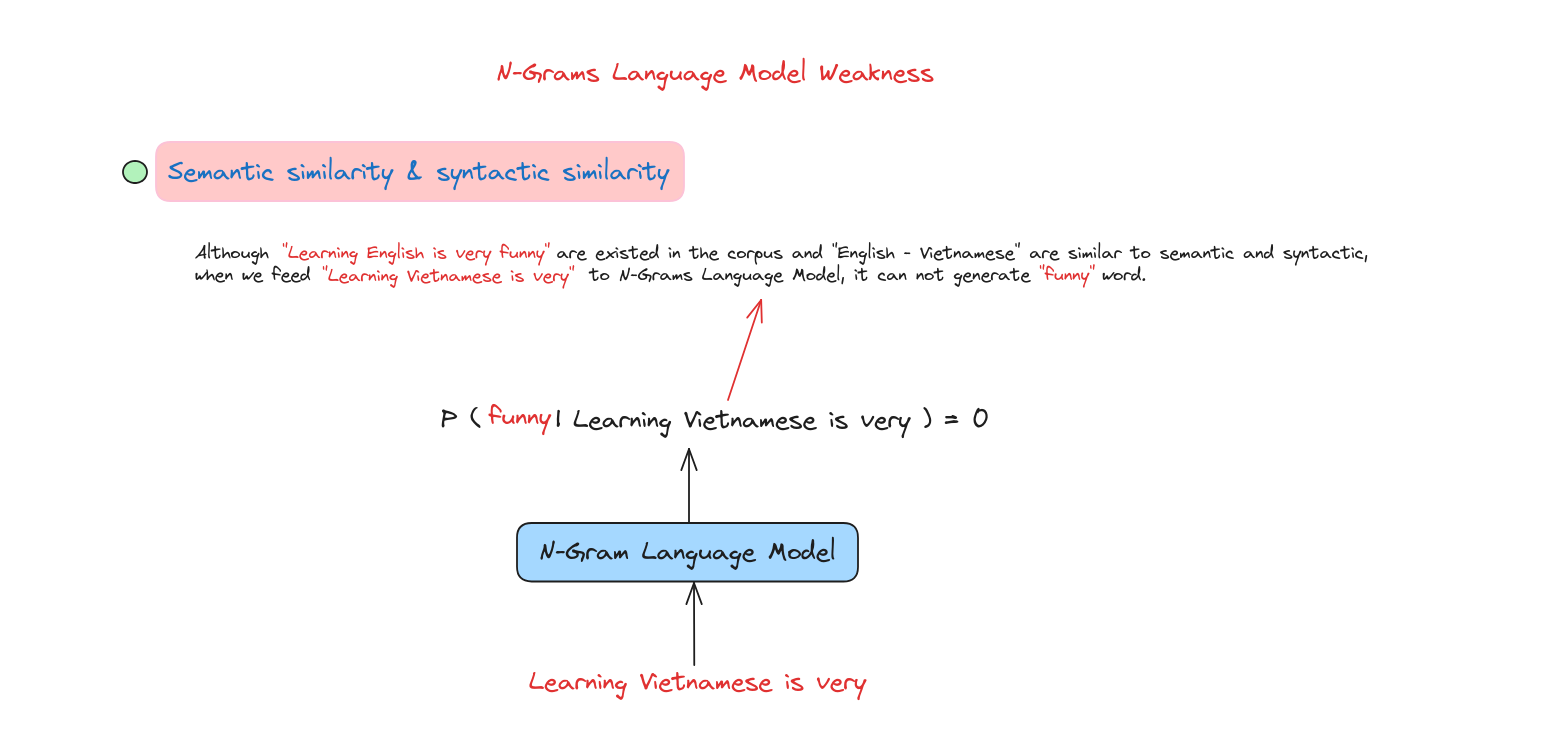
Chúng ta cần một mô hình ngôn ngữ mới để giải quyết các vấn đề này.
Mô hình ngôn ngữ dùng mạng nơ-ron
Neural language model là mô hình ngôn ngữ sử dụng mạng nơ-ron nhân tạo, lấy cảm hứng từ cấu trúc não bộ con người, để xử lý và sinh ngôn ngữ. Khi được huấn luyện trên tập dữ liệu lớn, nó học được các mẫu và mối quan hệ trong ngôn ngữ, cho phép thực hiện các tác vụ như sinh văn bản, dịch, phân tích cảm xúc với độ chính xác cao.
Các thành phần của RNN
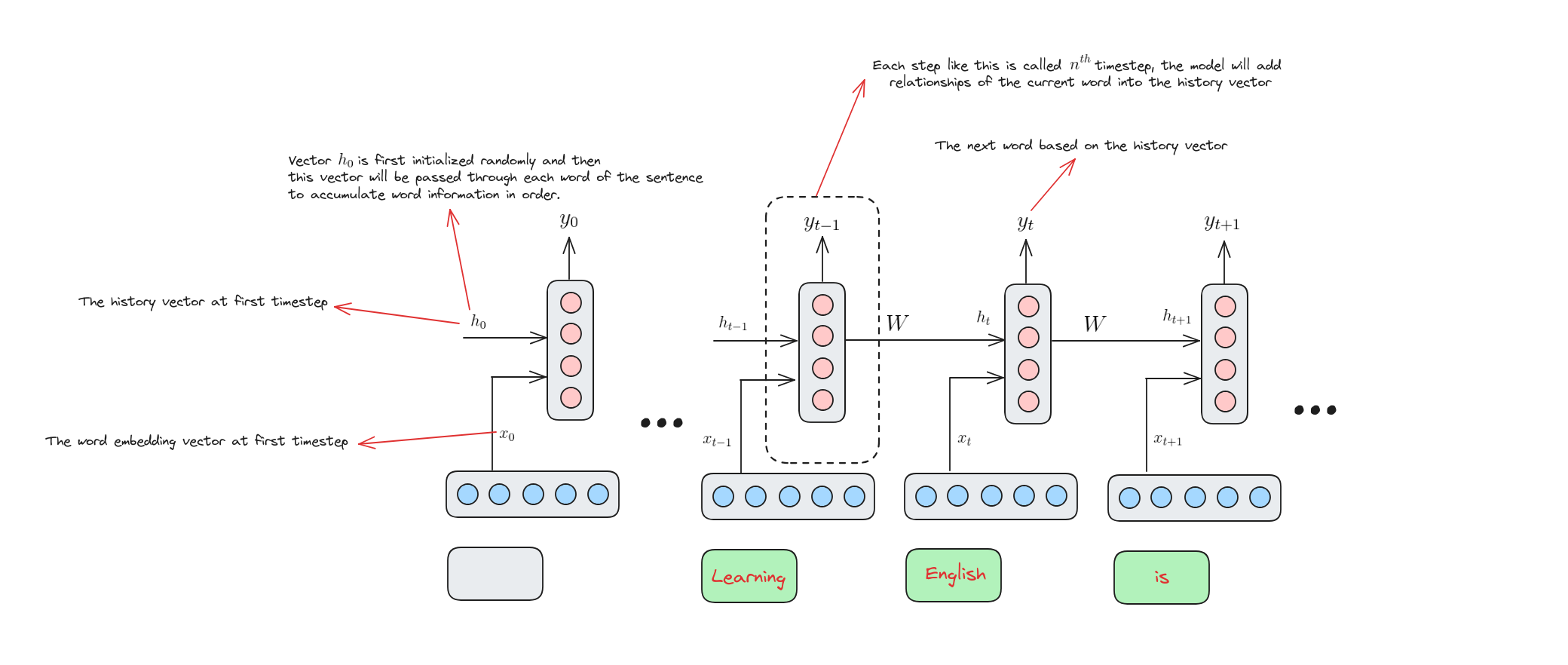
Mô hình ngôn ngữ dựa trên RNN
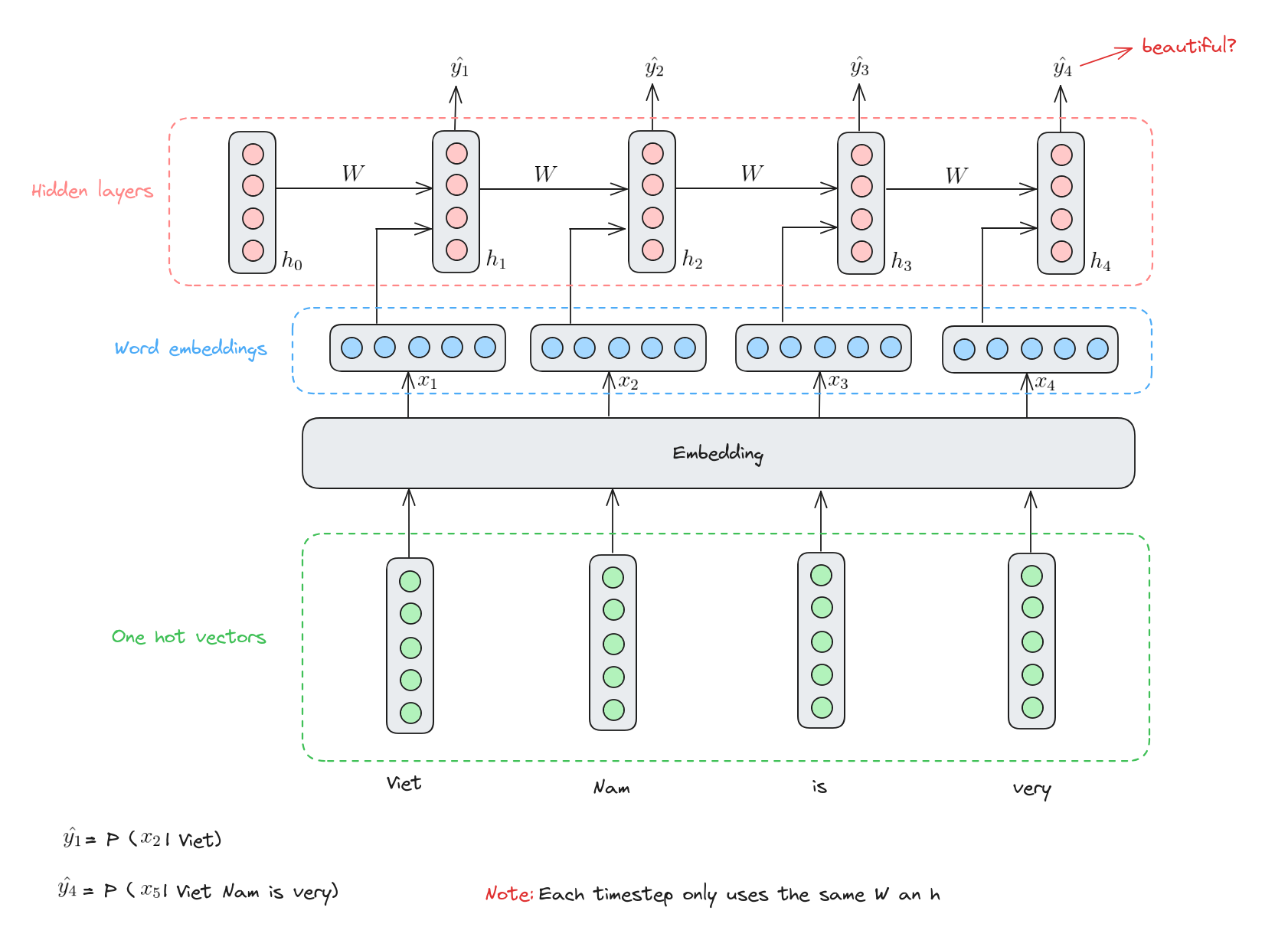
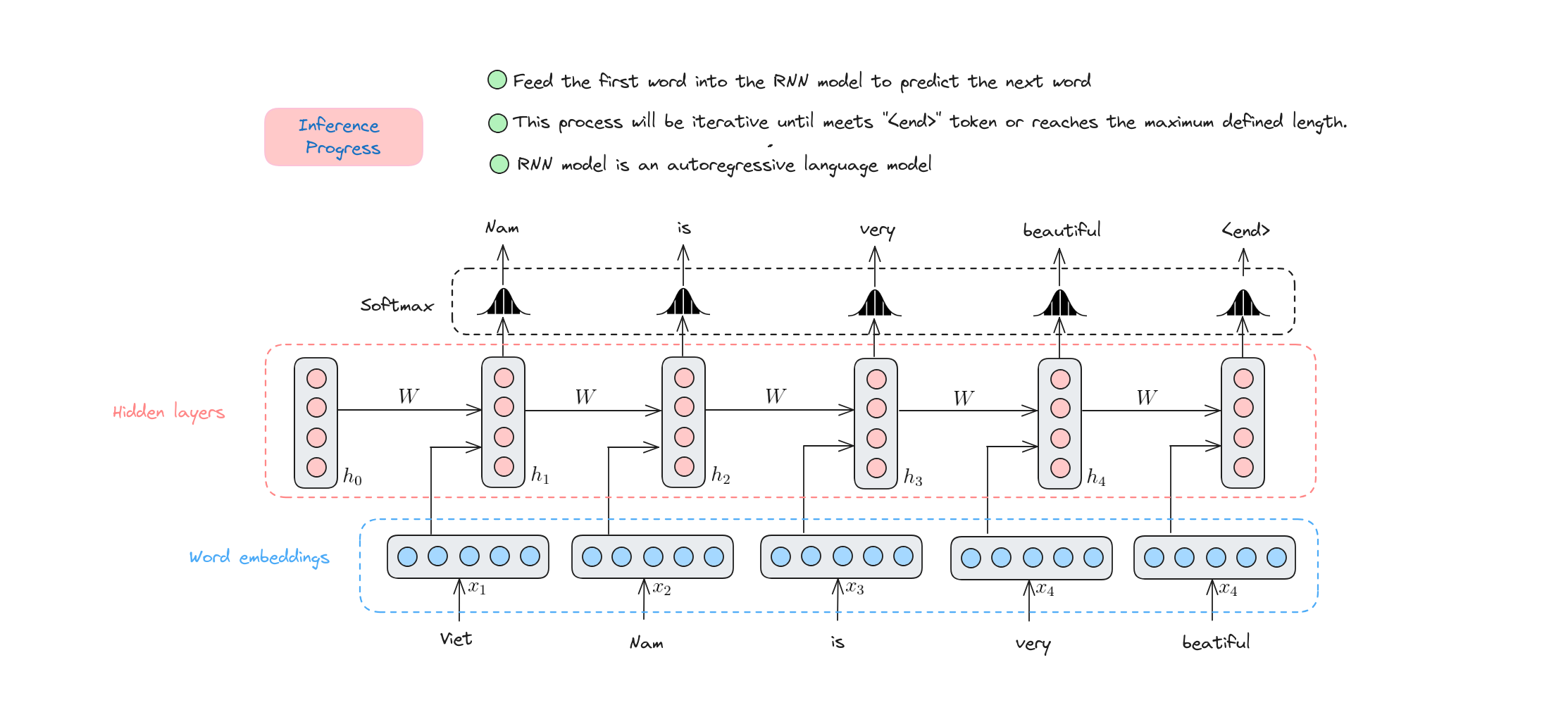
Quá trình suy luận của RNN
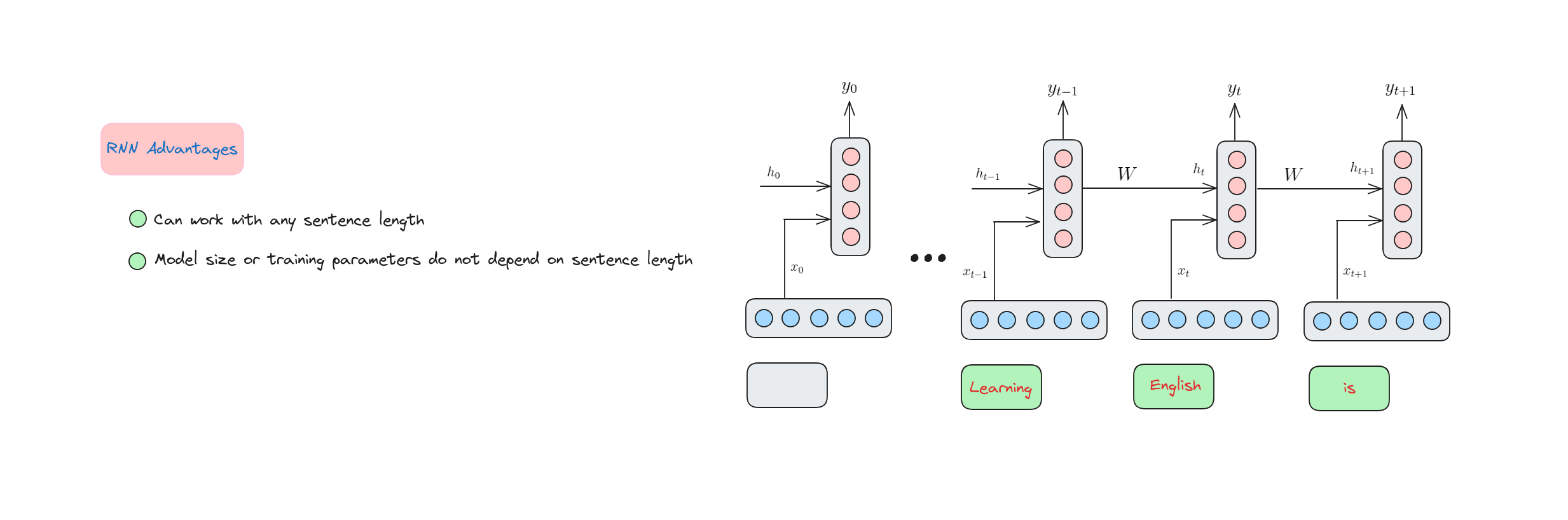
Ưu điểm của RNN
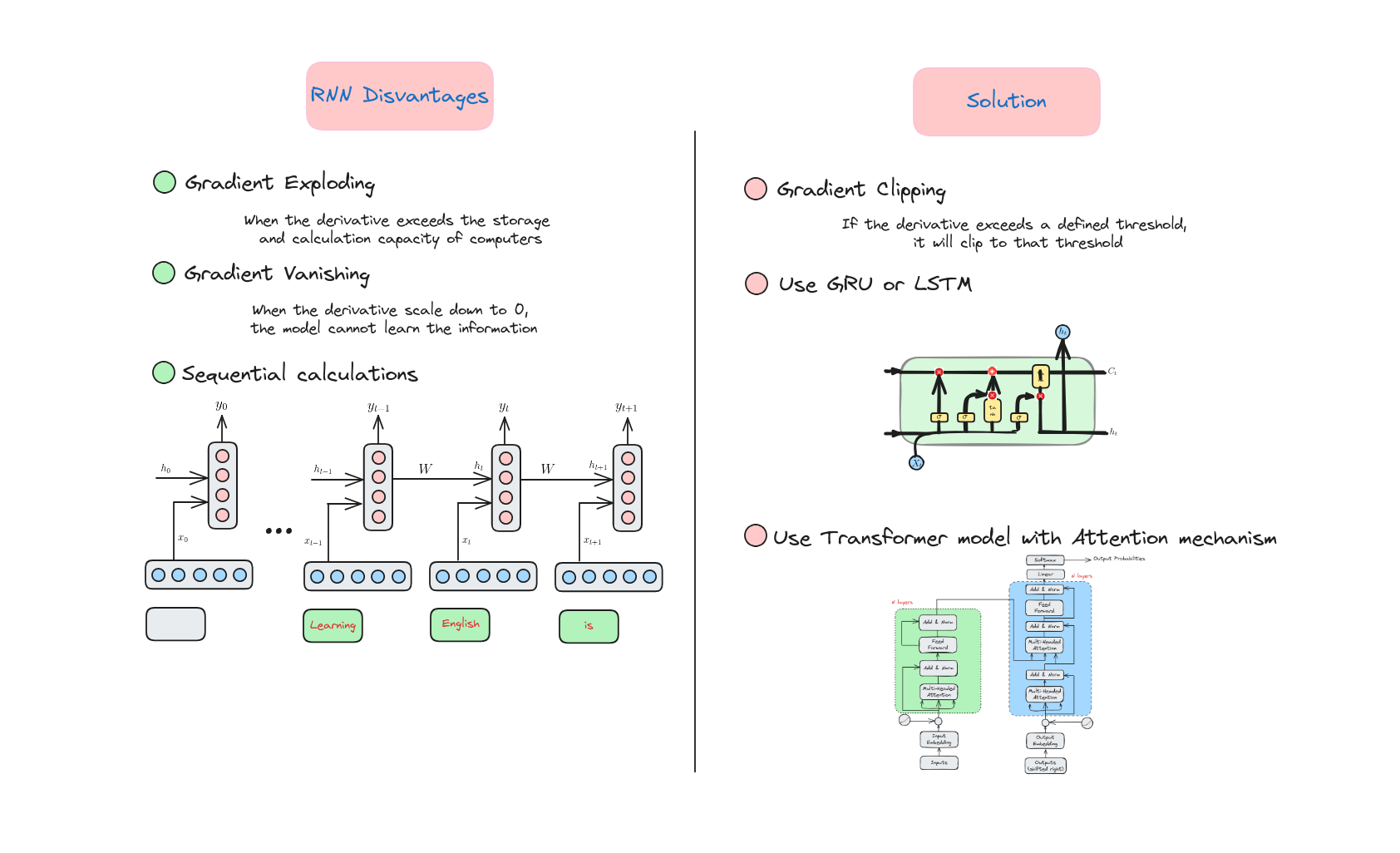
Vấn đề và giải pháp của RNN
Triển khai mô hình RNN
Trong phần này, chúng ta sẽ xây dựng một mô hình RNN để sinh văn bản.
Tải dữ liệu
!wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/dunghoang369/data/master/data.txt
Import các thư viện cần thiết (Import necessary libraries)
import numpy as np
import tensorflow.keras.utils as ku
from tensorflow.keras import regularizers
from tensorflow.keras.optimizers import Adam
from tensorflow.keras.models import Sequential
from tensorflow.keras.preprocessing.text import Tokenizer
from tensorflow.keras.preprocessing.sequence import pad_sequences
from tensorflow.keras.layers import Embedding, SimpleRNN, Dense, Dropout, Bidirectional
Tải dữ liệu vào bộ nhớ (Load data)
data = open('data.txt').read()
corpus = data.lower().split("\n")
# Hiển thị một số câu trong tập dữ liệu
print(corpus[:4])
['from fairest creatures we desire increase,',
"that thereby beauty's rose might never die,",
'but as the riper should by time decease,',
'his tender heir might bear his memory:']
Xây dựng tokenizer (Build tokenizer)
tokenizer = Tokenizer()
tokenizer.fit_on_texts(corpus)
# Đếm số lượng từ trong từ điển
total_words = len(tokenizer.word_index) + 1 # 1 cho oov (out-of-vocabulary) token
Total words: 3211
Tiền xử lý dữ liệu (Preprocess data)
Chúng ta sẽ tách mỗi câu thành các phần nhỏ hơn với độ dài tăng dần để tạo thành từng điểm dữ liệu.
input_sequences = []
for line in corpus:
token_list = tokenizer.texts_to_sequences([line])[0]
for i in range(1, len(token_list)):
n_gram_sequence = token_list[:i+1]
input_sequences.append(n_gram_sequence)
Kết quả dữ liệu sẽ như sau:
for point in input_sequences[:10]:
print(" ".join(tokenizer.sequences_to_texts([point])))
from fairest
from fairest creatures
from fairest creatures we
from fairest creatures we desire
from fairest creatures we desire increase
that thereby
that thereby beauty's
that thereby beauty's rose
that thereby beauty's rose might
that thereby beauty's rose might never
Padding toàn bộ tập dữ liệu (Padding whole dataset)
# pad sequences
max_sequence_len = max([len(x) for x in input_sequences])
input_sequences = np.array(pad_sequences(input_sequences, maxlen=max_sequence_len, padding='pre'))
Chúng ta sẽ thêm số 0 vào đầu các input_sequences để tạo các câu có cùng độ dài. Việc thêm 0 vào đầu là vì trong bài toán này ta sinh từ từ phía sau, nên thông tin bên phải phải là các giá trị khác 0.
Tách chuỗi thành đặc trưng và nhãn (Split sequence into features and label)
features, label = input_sequences[:,:-1],input_sequences[:,-1]
for i in range(10):
print("{} ---> {}".format(" ".join(tokenizer.sequences_to_texts(features[i:i+1])), tokenizer.sequences_to_texts([label[i:i+1]])[0]))
from ---> fairest
from fairest ---> creatures
from fairest creatures ---> we
from fairest creatures we ---> desire
from fairest creatures we desire ---> increase
that ---> thereby
that thereby ---> beauty's
that thereby beauty's ---> rose
that thereby beauty's rose ---> might
that thereby beauty's rose might ---> never
Chuyển nhãn sang vector one-hot
Chúng ta sẽ chuyển mỗi nhãn thành vector one-hot có độ dài bằng tổng số từ trong từ điển.
label = ku.to_categorical(label, num_classes=total_words)
Xây dựng mô hình RNN
model = Sequential()
model.add(Embedding(total_words, 100, input_length=max_sequence_len-1))
model.add(Bidirectional(SimpleRNN(150, return_sequences = True)))
model.add(Dropout(0.2))
model.add(SimpleRNN(100)) # h
model.add(Dense(total_words/2, activation='relu', kernel_regularizer=regularizers.l2(0.01)))
model.add(Dense(total_words, activation='softmax'))
model.compile(loss='categorical_crossentropy', optimizer='adam', metrics=['accuracy'])
print(model.summary())
Model: "sequential_4"
_________________________________________________________________
Layer (type) Output Shape Param #
=================================================================
embedding_4 (Embedding) (None, 10, 100) 321100
bidirectional_2 (Bidirecti (None, 10, 300) 75300
onal)
dropout_2 (Dropout) (None, 10, 300) 0
simple_rnn_3 (SimpleRNN) (None, 100) 40100
dense_4 (Dense) (None, 1605) 162105
dense_5 (Dense) (None, 3211) 5156866
=================================================================
Total params: 5755471 (21.96 MB)
Trainable params: 5755471 (21.96 MB)
Non-trainable params: 0 (0.00 Byte)
_________________________________________________________________
None
Huấn luyện mô hình RNN
history = model.fit(features, label, epochs=130, verbose=1)
Dự đoán 10 từ tiếp theo
test_seq = "despite of wrinkles this thy golden time more survey slain torn slain erred"
next_words = 10
for _ in range(next_words):
# Chuyển câu thành vector
token_list = tokenizer.texts_to_sequences([test_seq])[0]
# Padding câu
token_list = pad_sequences([token_list], maxlen=max_sequence_len-1, padding='pre')
# Dự đoán từ tiếp theo
predicted = model.predict(token_list, verbose=0)
output_word = ""
predicted_id = np.argmax(predicted)
if predicted_id in tokenizer.index_word:
output_word = tokenizer.index_word[predicted_id]
test_seq += " " + output_word
else:
break
print(test_seq)
Kết quả đầu ra:
despite of wrinkles this thy golden time more survey slain torn slain erred cross hate part new quite stand it words more words
Kết luận
Trong bài học này, chúng ta đã tìm hiểu:
- Mô hình ngôn ngữ N-Grams.
- Sự kỳ diệu của Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs) và khả năng xử lý dữ liệu tuần tự như văn bản, giọng nói. Chúng ta đã khám phá cách RNN ghi nhớ các đầu vào trước, giúp nó phù hợp cho các tác vụ cần ngữ cảnh.
- Ưu điểm và nhược điểm của RNN.
Tài liệu tham khảo
- A. Amidi and S. Amidi, “CS 230 - Recurrent Neural Networks Cheatsheet,” Stanford.edu, 2019. https://stanford.edu/~shervine/teaching/cs-230/cheatsheet-recurrent-neural-networks
- “Recurrent Neural Network Tutorial (RNN),” www.datacamp.com. https://www.datacamp.com/tutorial/tutorial-for-recurrent-neural-network